C# Operators and Expressions
Operators and expressions in C#: arithmetic, comparison, logical, increment/decrement, ternary, and null-coalescing usage.
In C#, operators are special symbols that perform operations on variables or values. With these symbols, you can do mathematical calculations, compare two values, build logical conditions, or quickly assign a value to a variable. Structures formed by combining operators are called expressions. Expressions are the fundamental building blocks that drive program flow and produce results.
Assignment Operator (=)
Used to assign a value to a variable.
int x = 5;
string message = "Hello";
x = 10;
Here, the value 5 is assigned to the variable x of type int, and the value "Hello" is assigned to the variable message of type string. Later, the value 10 is assigned to x.
Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used to perform numeric operations in C#. They handle basic math such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and modulus (remainder).
| Operator | Description | Example (x=10, y=3) |
Result |
|---|---|---|---|
+ |
Addition | x + y |
13 |
- |
Subtraction | x - y |
7 |
* |
Multiplication | x * y |
30 |
/ |
Division | x / y |
3 |
% |
Modulus (Remainder) | x % y |
1 |
Example:
int a = 15;
int b = 4;
Console.WriteLine(a + b); // 19
Console.WriteLine(a / b); // 3
Console.WriteLine(a % b); // 3
Comparison Operators
Comparison operators in C# are used to compare two values. The result of these operations is always of type bool.
bool is a logical data type that can only take the values true or false.
| Operator | Description | Example (x=10, y=3) |
Result |
|---|---|---|---|
== |
Equal to | x == y |
false |
!= |
Not equal to | x != y |
true |
> |
Greater than | x > y |
true |
< |
Less than | x < y |
false |
>= |
Greater than or equal to | x >= y |
true |
<= |
Less than or equal to | x <= y |
false |
Example:
int a = 7;
int b = 10;
bool result1 = (a < b); // true
bool result2 = (a == b); // false
Console.WriteLine(result1); // true
Console.WriteLine(result2); // false
Logical Operators
Used to combine conditions. These conditions are of type bool. They perform the logical operations and, or, and not.
| Value 1 | Value 2 | && (and) | || (or) |
|---|---|---|---|
true |
true |
true |
true |
true |
false |
false |
true |
false |
true |
false |
true |
false |
false |
false |
false |
Operators are used as follows:
| Operator | Description | Example (a=true, b=false) |
Result |
|---|---|---|---|
&& |
and | a && b |
false |
|| |
or | a || b |
true |
! |
not | !a |
false |
For example, if variable x is less than 5 and variable y is greater than 10, you can write the condition as:
bool crit = x < 5 && y > 10;
A simple example that states the user can drive if they are over 18 and have a driver’s license:
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Console.Write("Enter your age: ");
int age = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Do you have a driver's license? (Y/N): ");
string answer = Console.ReadLine().ToUpper();
bool hasLicense = (answer == "Y");
if (age >= 18 && hasLicense)
{
Console.WriteLine("You can drive a car.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("You cannot drive a car.");
}
}
}
Compound Assignment Operators
Combine assignment with arithmetic. For example, add 5 to a number, subtract 2, or multiply it by 6.
| Operator | Description | Example (x=10) |
Result |
|---|---|---|---|
+= |
add | x += 5 |
15 |
-= |
subtract | x -= 2 |
8 |
*= |
multiply | x *= 6 |
60 |
/= |
divide | x /= 2 |
5 |
%= |
modulus | x %= 2 |
0 |
Increment and Decrement Operators
Used to increase or decrease a number by 1.
int x = 5;
x++; // 6
x--; // 5
Prefix vs. Postfix:
int a = 5;
Console.WriteLine(++a); // 6 (increment first, then print)
Console.WriteLine(a++); // 6 (print first, then increment → a=7)
Ternary Operator (?:)
A short form of if-else. Conditionally selects one of two values.
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Console.Write("Enter a number: ");
int num = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
string result = (num % 2 == 0)
? "The number you entered is even."
: "The number you entered is odd.";
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
}
- The number is read with
Console.ReadLine(). - Converted from
stringtointwithint.Parse. - The ternary (
?:) checksnum % 2 == 0. - The result message is printed to the screen.
Null-Coalescing Operators (?? and ??=)
In C#, null indicates that a variable does not reference any value. In other words, the variable is defined but contains no value. This commonly appears with string or class (reference type) variables.
Sometimes we want to assign a default value instead of a null one. This is where the null-coalescing operators come into play:
Example 1: Using ??
string name = null;
string result = name ?? "Anonymous";
Console.WriteLine(result);
Example 2: Using ??=
string name = null;
name ??= "Unknown";
Console.WriteLine(name); // Unknown
Example (Shopping Cart)
using System;
using System.Globalization;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// Input culture: reduce dot/comma issues
CultureInfo.CurrentCulture = CultureInfo.InvariantCulture;
// 1) Get user inputs one after another
Console.Write("Name (you may leave it blank): ");
string name = Console.ReadLine();
name = string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(name) ? null : name.Trim();
name ??= "Guest"; // (??=) assign default name if null
Console.Write("City (you may leave it blank): ");
string city = Console.ReadLine();
city = string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(city) ? null : city.Trim();
string cityInfo = city ?? "Unknown City"; // (??) value to display if null
Console.Write("Cart total (e.g., 749.90): ");
double cartTotal = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Are you a member? (Y/N): ");
bool isMember = Console.ReadLine().Trim().ToUpper() == "Y";
Console.Write("Coupon code (you may leave it blank): ");
string coupon = Console.ReadLine();
coupon = string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(coupon) ? null : coupon.Trim().ToUpper();
Console.Write("Would you like express shipping? (Y/N): ");
bool express = Console.ReadLine().Trim().ToUpper() == "Y";
// 2) Business rules and operators
// Arithmetic: VAT, discount, shipping, total
const double VatRate = 0.20; // 20% VAT
const double MemberDisc1 = 0.05; // 5% if member
const double MemberDisc2 = 0.10; // 10% if member and cart >= 500
const double CouponDisc = 0.10; // +10% if coupon is "INDIRIM10"
const double MaxDiscount = 0.25; // Discount cap at 25%
const double StdShipping = 19.90;
const double ExpressShipping = 49.90;
const double FreeShippingThreshold = 300.0;
// Comparison + logical: determine discount rate
double discountRate = isMember && cartTotal >= 500
? MemberDisc2
: (isMember ? MemberDisc1 : 0.0); // (?:) ternary
// Logical: coupon check (OR)
if (coupon == "DISCOUNT10" || coupon == "CODE10")
discountRate += CouponDisc; // Compound assignment (+=)
// Apply cap
discountRate = Math.Min(discountRate, MaxDiscount);
// Calculate discount and VAT
double discountAmount = cartTotal * discountRate; // (*)
double subTotal = cartTotal - discountAmount; // (-)
double vat = subTotal * VatRate; // (*)
// Shipping: express? otherwise check free-shipping threshold
double shipping = express
? ExpressShipping
: (subTotal >= FreeShippingThreshold ? 0.0 : StdShipping);
// Grand total
double grandTotal = subTotal + vat; // (+)
grandTotal += shipping; // Compound assignment (+=)
// 3) Summary output
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("— Payment Summary —");
Console.WriteLine($"Customer : {name} ({cityInfo})");
Console.WriteLine($"Cart : {cartTotal:0.00} £");
Console.WriteLine($"Discount % : {(discountRate * 100):0}% (-{discountAmount:0.00} £)");
Console.WriteLine($"Subtotal : {subTotal:0.00} £");
Console.WriteLine($"VAT (20%) : {vat:0.00} £");
Console.WriteLine($"Shipping : {shipping:0.00} £ {(express ? "(Express)" : "(Standard)")}");
Console.WriteLine($"Grand Total : {grandTotal:0.00} £");
// Extra logical example: invoice note
bool highCart = grandTotal >= 1000.0;
Console.WriteLine(highCart && isMember
? "Note: You earned extra points for your high-value order."
: "Note: Become a member to benefit from extra discounts.");
}
}
With this example, you can try a console application that combines the topics above.
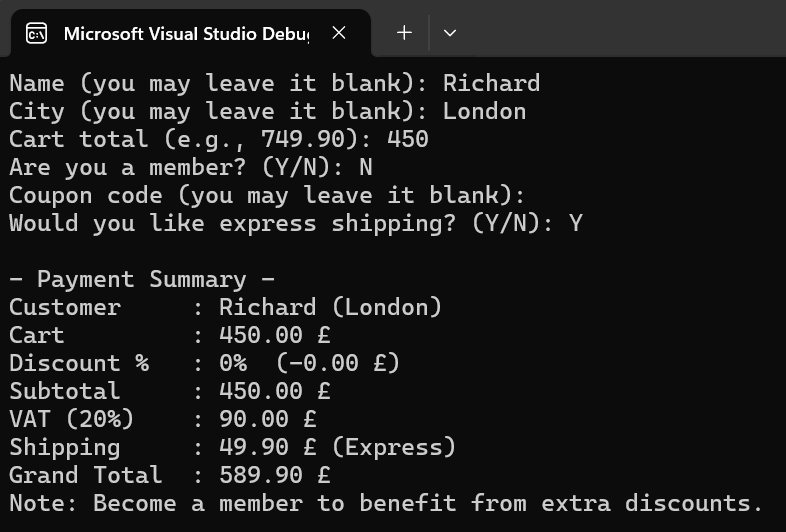
The application output will look like the screenshot above.
Related Articles
C# Basic Data Types
Basic data types in C#: numeric, text, logical, object-based, and nullable types.
C# Boolean Operations
Learn how boolean operations work in C#, including the bool type, comparisons, and logical operators like &&, ||, and ! with examples.
C# Conditional Statements (if, else, switch)
Decision structures in C#: learn how to use if, else if, else and switch to perform different actions based on conditions.
C# Math Library
Learn how to use the C# Math library, including Pow, Sqrt, Round, Abs, and other essential mathematical methods with examples.
C# Syntax Structure
Learn the basics of C# syntax, including code blocks, comments, and variable naming rules, with clear explanations and practical examples.
Lambda Expressions in C#
Learn lambda expressions in C#, including concise syntax, Func and Action delegates, and practical LINQ usage examples.