C# Basic Data Types
Basic data types in C#: numeric, text, logical, object-based, and nullable types.
In C#, data is stored using different types, and each data type defines how much memory is used and which operations can be performed. These types play a key role in how a program behaves. In this article, we will explore numeric, textual, logical, dynamic, and nullable data types with practical examples.
Choosing the right data type is a crucial part of learning C#. Proper type selection improves performance, optimizes memory usage, and helps prevent common programming errors. Understanding the fundamental data types early on provides a solid foundation for building reliable applications.
Numeric Types
Numeric types are used for integers and floating-point numbers. For financial calculations, decimal is recommended.
| Type | Description | Example | Memory |
|---|---|---|---|
int | Integer (−2B - +2B) | 42 | 4 bytes |
long | Larger integers | 100000000 | 8 bytes |
short | Small integers | 120 | 2 bytes |
byte | 0 - 255 positive | 200 | 1 byte |
double | Floating-point (double precision) | 3.14 | 8 bytes |
float | Floating-point (single precision) | 2.5f | 4 bytes |
decimal | Decimal for financial use | 19.99m | 16 bytes |
int age = 25;
double pi = 3.14159;
decimal price = 19.99m;
Console.WriteLine(age);
Console.WriteLine(pi);
Console.WriteLine(price);
Note: For financial calculations, decimal is preferred over double because it avoids floating-point rounding errors and provides higher precision.
Text Types
char holds a single character, while string holds a sequence of characters.
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
char | Single character | 'A', '9' |
string | Text / sequence of characters | "Hello World" |
char firstLetter = 'M';
string message = "Hello";
Console.WriteLine(firstLetter);
Console.WriteLine(message);
Logical Type
bool can only hold true or false. It is widely used in conditions.
bool isStudent = true;
bool isGraduate = false;
Console.WriteLine(isStudent);
Console.WriteLine(isGraduate);
Object and Dynamic Types
object, var, and dynamic are used for flexible usage.
object data = 42;
var text = "Hello";
dynamic variable = 5;
variable = "Now it's a string";
Console.WriteLine(data);
Console.WriteLine(text);
Console.WriteLine(variable);
Nullable Types
Value types (e.g. int, double, bool) cannot be null by default. Adding ? allows them to be nullable.
int? grade = null;
if (grade == null)
Console.WriteLine("No grade entered.");
else
Console.WriteLine($"Grade: {grade}");
When Should Each Data Type Be Used?
- int: Counters, age values, quantities, and whole numbers
- double: Physical measurements and approximate calculations
- decimal: Monetary values, prices, and financial calculations
- string: Text input received from the user
- bool: Conditions, comparisons, and control flow logic
Assignments Between Data Types and Type Conversions
In C#, variables of different data types cannot always be assigned to each other directly. Attempting to assign incompatible types results in a compile-time error.
Invalid Assignments
int number = 10;
string text = number; // ERROR
bool flag = true;
int value = flag; // ERROR
In the examples above, the assignments fail because the data types are not compatible.
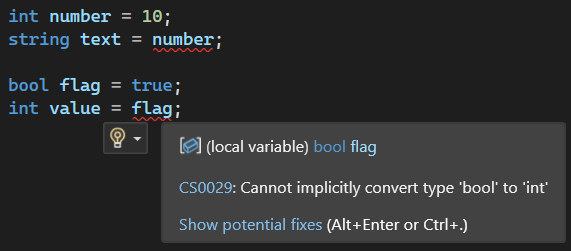
In the image above, Visual Studio immediately detects invalid assignments between incompatible data types. The example shows attempts to assign values between types such as bool and int, which are not directly compatible. The editor highlights the issue with a red underline and displays a compile-time error like CS0029.
Implicit Conversions
int small = 5;
double large = small; // Valid
Smaller numeric types can be automatically converted to larger numeric types.
Explicit Conversions
double pi = 3.14;
int wholeNumber = (int)pi; // 3
Conversions that may cause data loss or precision loss require explicit casting.
Summary
- Numbers:
int,double,decimal - Text:
char,string - Logical:
bool - Flexible:
object,var,dynamic - Nullable: with
?
Related Articles
Arrays in C#
Learn arrays in C#, including declaration, indexing, looping through elements, and common array operations with examples.
C# Operators and Expressions
Operators and expressions in C#: arithmetic, comparison, logical, increment/decrement, ternary, and null-coalescing usage.
C# String Operations
Learn how to work with strings in C#, including concatenation, searching, substring, IndexOf, and other essential string operations.
C# Syntax Structure
Learn the basics of C# syntax, including code blocks, comments, and variable naming rules, with clear explanations and practical examples.
C# Type Conversions
Learn how type conversions work in C#, including implicit and explicit casting, Parse, TryParse, and Convert methods with examples.
Interop in C# (Working with C/C++ Libraries)
Learn how to use Interop in C# to work with C/C++ libraries, including P/Invoke, unmanaged code, and data marshaling.
Introduction to C# and the .NET Ecosystem
C# is a modern, safe, and object-oriented language. With the .NET ecosystem, it is possible to develop web, mobile, desktop, and game applications.